
One of the trickiest parts of running a business is inventory management. How do you make sure you have enough stock to meet customer demand? How do you avoid overstocking and incurring unnecessary costs?
When they’re reordering products, most businesses tend to place orders based on what they need at the exact moment.
That’s not very optimal.
You should be optimising the way you order and pay for products by understanding and using the economic order quantity formula.
Knowing EOQ calculation helps you save money on third party logistics and fulfilment warehousing costs. It also helps you make better decisions about how much product you should be ordering in a given period of time.
EOQ: What Does it Mean?
Economic order quantity (EOQ) is a formula that businesses use to figure out the optimal number of inventory units to order. The goal is to minimise the costs associated with ordering, holding, and storing inventory.
You want to avoid ordering too much or too little. Your business has to run smoothly without too much overhead costs or stock shortages. The EOQ model is useful for businesses that manage large amounts of stock or deal with fluctuating demand.
How To Calculate EOQ
To properly calculate the EOQ, there’s some data that you’ll need. Most of it is going to be historical data, so the economic quantity order formula works best if you’ve been doing business and fulfilling orders for at least a year.
The EOQ formula depends on three key variables:
- Order cost (O): This is the fixed cost associated with making an order. It includes any shipping, handling and administration costs you incur when ordering goods.
- Holding costs (H): It’s also known as your carrying cost. This will include storage costs, fulfilment costs, labour costs, total cost of inventory, insurances, and depreciation costs.
- Demand (D): The annual demand of your goods. Check your sales over the past year to find out what your annual demand is.
The economic order quantity equation is:
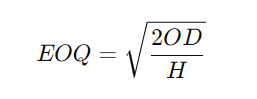
Let’s clarify this further with an example.
Say you want to calculate the economic order quantity for your brand’s most popular product: a custom strawberry-scented perfume. After doing some research, you find out that your:
- Order cost (O) is $200
- Holding cost (H) is $1.50 per unit
- Demand rate (D) is 20,000 units per year
Let’s perform the calculations.
EOQ = √ [(2 x 200 x 20,000) / 1.50]
EOQ = √ [8,000,000 / 1.50]
EOQ = √ 5,333,333.33
EOQ = 2,309 units per order
According to the EOQ formula, the optimal number of inventory units for your bestseller in a given restocking order is 2,309 units.
Benefits Of Using The EOQ Equation For Inventory Management
Calculating EOQ and implementing it for your business can benefit you in many ways — mostly your bottom line. It’s a great way to figure out how much inventory you need to purchase to maintain an efficient e-commerce supply chain while keeping costs at a minimum.
1. Reduced inventory costs overall
Extra items in your inventory can quickly increase storage costs. The cost of inventory also goes up depending on how you order, which products are damaged, and which of your products never sell.
By calculating the right order size through EOQ, you can avoid overordering. With this, you reduce unnecessary storage expenses and minimise the risk of damage or product obsolescence.
2. Prevent stockouts
Nothing can hurt your business more than running out of stock for a popular item. With EOQ, you can calculate how much you need based on how much you’re selling in a given time period. Your business can maintain the right inventory levels, and you can prevent stock outs without keeping too much inventory on hand for too long.
Calculating EOQ can also help you uncover interesting insights. Perhaps you’ll discover that your business is better off when you order smaller quantities, or maybe you’ll find out that it’s more cost-effective to order in bulk.
Either way, this is information you’ll only know if you calculate your EOQ.
3. Improved cash flow
By ordering only the ideal amount of stock, you free up cash that would otherwise be tied up in excess inventory. You can reinvest this cash in other critical areas of your business, such as marketing, product development, or improving customer service.
4. Data-driven decision-making
EOQ is based on historical data and it can guide your inventory decisions in a more informed manner. Instead of relying on guesswork, EOQ gives you tangible numbers and proven calculations that suggest the best order quantity.
A data-driven approach helps you make smarter business decisions that optimise your business operations and reduce risks.

How To Implement EOQ In Your Business
After understanding the benefits of EOQ, the next step is to put it into practice. Here’s how to introduce EOQ into your inventory management process:
Step 1: Gather the required data.
Ensure that all information — the costs, demands, and holding costs — are as up-to-date as possible to get reliable results. Historical data from at least one year is ideal, as this will give you a clearer picture of your business’ demand patterns.
Step 2: Calculate your EOQ.
Input your data into the EOQ formula to find the optimal order quantity. There are also several tools and software that can assist you with EOQ calculations to ensure accuracy and reduce the time spent on manual work.
Step 3: Implement and Monitor
After calculating the EOQ, integrate it into your ordering process. It’s integral to monitor how well EOQ is working and adjust as necessary, especially if demand patterns or supplier costs fluctuate over time. Regularly updating your EOQ keeps your inventory strategy effective as time goes on.
The Common Challenges And Limitations Of EOQ
EOQ is a powerful tool for maintaining a good inventory balance, but it’s not without its pitfalls. Here are some of the most common issues businesses face when implementing EOQ.
1. Inaccurate demand forecasting
Demand rate is an important element in the EOQ formula, but anyone who runs a business knows that demand doesn’t always adhere to your expectations. If there are fluctuations in product demand — whether demand goes up or down, using the EOQ that was previously calculated can lead you to purchase too much or too little inventory.
To prevent this from happening, it’s important to track demand and order history carefully over time. To make it easier, brands partner up with order fulfilment centres like Green Fulfilment to get software solutions that automatically track order data and sales. You can then review this data to get a better and more reliable forecast demand in the future.
Key tip: the more frequently you can use the EOQ formula, the easier replenishing your inventory will be.
2. Changing supplier costs
Similar to how demand shifts over time, the price of the raw materials or wholesale products you sell in your store also change. This causes order costs to fluctuate, and it, in turn, impacts your EOQ’s accuracy and usefulness. If your costs to acquire inventory changes all the time, EOQ may not be the best tool for balancing your inventory levels.
3. It focuses on only one product
EOQ is calculated on a per-product basis. That means that one product’s EOQ may not be the same as a different product’s EOQ. If your business has lots of SKUs in their product catalogue, calculating EOQs for each product can be too tedious, time-consuming, or confusing.
To solve this issue, it’s wise for brands to invest in inventory management software like Green Fulfilment’s Green Portal. Green Portal lets you set automatic reorder point notifications for each SKU. Our software will alert you when SKUs levels dip below a certain point, so that they can order more. This can help you balance inventory levels without using EOQ.
4. It can ignore external factors
There is no fool-proof formula — even the EOQ. There will be unforeseeable circumstances that can affect your inventory balance. Spoilage, theft, unexpected supply chain issues and blockages are a few examples that can mess with your inventory levels. In turn, it also renders your previous EOQ calculations ineffective.
The smart way to cope with these unforeseen circumstances and work around the risks is to partner up with an experienced fulfilment centre, like Green Fulfilment. Fulfilment centres have the manpower, technology, and infrastructure to help businesses optimise inventory management in spite of unpredictable external factors like holiday rushes and global pandemics.urnover ratios down to SKU level, which lets you identify products that are not delivering sufficient ROI.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the formula for EOQ cost per order?
The formula:
Cost per Order = Ordering Cost / EOQ
- Ordering Cost: The fixed cost associated with placing an order, regardless of the quantity ordered.
- EOQ: The Economic Order Quantity is calculated using the EOQ formula.
- Cost per Order: This represents the average cost of placing an order for a given quantity.
The cost per order helps your business understand the fixed costs associated with ordering. It, in turn, optimises their inventory management strategies.
How do you calculate average inventory from EOQ?
The formula:
Average Inventory = EOQ / 2
- EOQ: The Economic Order Quantity.
- Average Inventory: The average level of inventory maintained over a given period.
- EOQ / 2: Assuming a constant demand rate and instant replenishment, the inventory level will fluctuate between 0 and EOQ. The average inventory is therefore the midpoint of this range.
The average inventory formula helps you manage cash flow by minimising the amount of capital tied up in inventory.
How to calculate holding cost in EOQ?
The formula:
Holding Cost = Average Inventory x Holding Cost per Unit
- Holding Cost per Unit: The cost of holding one unit of inventory for a specific period.
- Holding Cost: The total cost of holding inventory over a given period.
The holding cost formula optimises their inventory management by balancing the costs of holding inventory with the benefits of having it available.
What is the formula for reorder level in EOQ?
The formula:
Reorder Level = Lead Time Demand + Safety Stock
- Lead Time Demand: The expected demand for the product during the time it takes to replenish the inventory (lead time).
- Safety Stock: Additional inventory held to buffer against uncertainties in demand or lead time.
- Reorder Level: The inventory level at which a new order should be placed to ensure that the stockout risk is minimised.
The reorder level in EOQ helps you avoid lost sales and customer dissatisfaction because of insufficient inventory.
What is the formula for the inventory cycle in EOQ?
The formula:
Inventory Cycle = EOQ / Annual Demand
- Annual Demand: The total demand for the product over a year.
- Inventory Cycle: The time between placing an order and receiving the next order.
The purpose of the inventory cycle in EOQ is to help businesses plan their inventory management and optimise their supply chain operations.
Can EOQ be used for perishable items or products with seasonal demand?
Yes, it can, but there should be some adjustments. EOQ works best for products with steady demand. For seasonal or perishable items, you may need to adjust your calculations based on fluctuations in demand.
Final Thoughts
EOQ is a game-changer for businesses who want to optimise their inventory management. It comes with its own set of challenges and manageable solutions, but the benefits outweigh the difficulties.
Calculating EOQ is impossible without the proper data, and that’s why Green Fulfilment has the inventory management software, Green Portal. It helps you track how much inventory you’re moving per day, week, month, or year. It also tells you your order and holding costs.
Combining Green Portal’s other features and tools with EOQ calculations help you save more money in the long run, freeing up capital so you can grow your business efficiently.
