
Proper inventory management is key for success in e-commerce. One important part of this is using SKU numbers. But what is a SKU, and how can they help your business?
This article will look at SKU numbers, explaining their importance and how to implement them effectively in your e-commerce operations. Whether you’re a small start-up or an established online retailer in the UK, you will need to understand how SKUs work and how to use them to improve your inventory management.
We’ll cover everything from the basics of SKU numbers to advanced implementation strategies. This is knowledge that you need for optimising your inventory management processes.
Let’s begin by exploring the meaning of SKU and why they’re so important in e-commerce.
What is a SKU number?
A Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is a unique alphanumeric code used by retailers and fulfilment centres, like Green Fulfilment, to identify and track products. Each item in a company’s inventory is assigned its own unique SKU for precise management and monitoring.
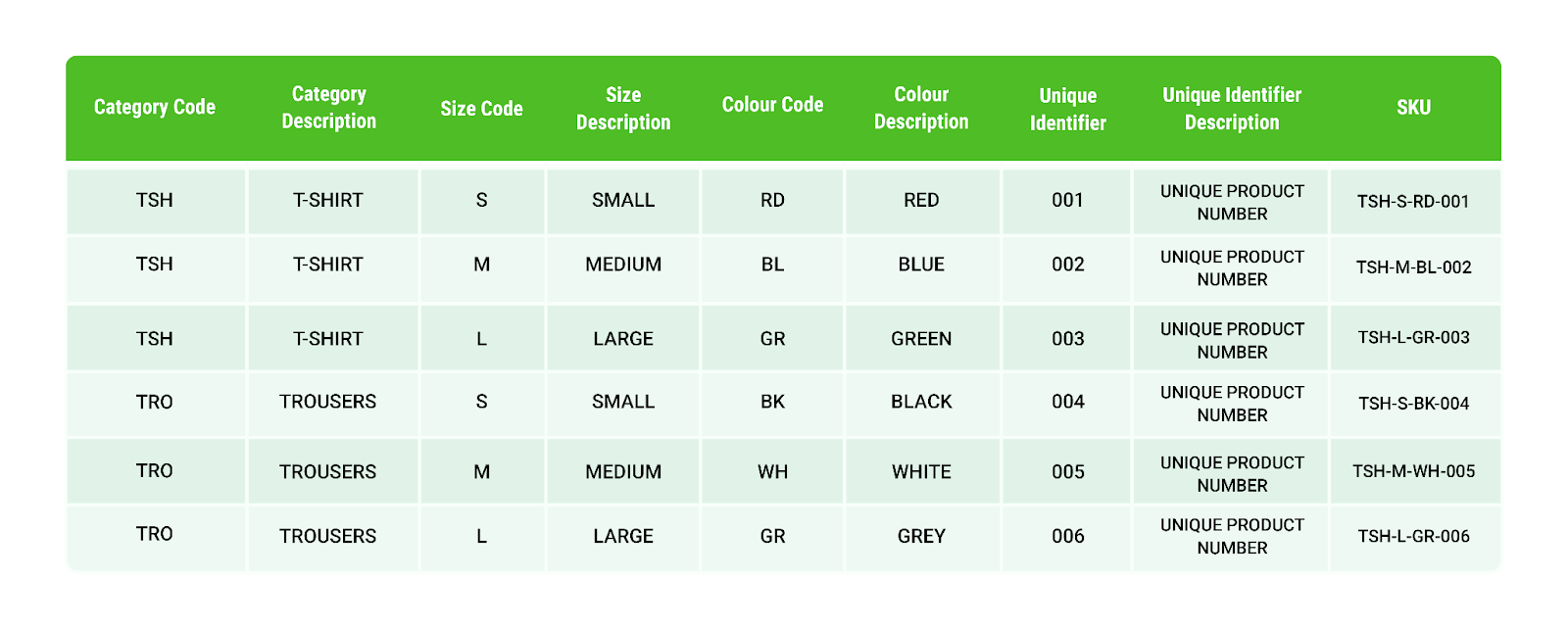
SKUs typically range from 8 to 12 characters in length. These codes incorporate various product characteristics, such as category, size, colour, and price. For instance, a SKU code for a red t-shirt might be TRS-M-RD-001. TRS stands for t-shirt, M for medium size, RD for red, and 001 as a unique identifier.
Unlike universal product codes (UPCs), SKUs are created by individual businesses to suit their specific needs. Customisation like this allows retailers and fulfilment warehouses, like Green Fulfilment, to tailor their inventory tracking system to their unique product range and operational requirements.
Implementing an effective SKU system helps businesses improve their inventory management. It also streamlines order processing and improves overall efficiency in their e-commerce operations. For companies using fulfilment services, well-structured SKUs are essential for seamless integration and accurate order fulfilment.
What are the benefits of using SKUs in your store?
A robust SKU numbers system benefits your e-commerce business in 3 ways:
1. Efficient inventory tracking
SKU codes are important for tracking inventory in multiple locations. They provide the following:
- Real-time visibility of stock levels at different warehouses
- Quick identification of low-stock items
- Efficient transfer of products between locations
For instance, a clothing retailer is capable of instantly checking if a particular size and colour of a T-shirt is available in any of their warehouses. This results in quick order fulfilment.
2. Improvement on sales data analysis
SKUs and their stock number lookup capabilities give businesses useful insights that can be used for sales analysis. This includes:
- Tracking the performance of each product variant.
- Identifying best-sellers and slow-moving items.
- Analysing sales trends according to product attributes like colour, size, and season.
This data enables you to make informed decisions about restocking, promotions, and future product offerings. This is especially valuable when working with a fulfilment warehouse. Data like this helps optimise inventory levels and streamline operations.
3. A better customer experience
SKUs improve customer satisfaction through:
- Ensuring product availability: Accurate SKU management lets businesses set up automatic reordering systems to prevent out of stock issues.
- Alternative offerings: If a product is out of stock, an e-commerce platform can use SKUs to suggest similar items. Businesses can potentially recover the sale and improve the user experience at the same time.
Here’s an example: A customer goes to an online store, searches for a blue dress in size 10, and finds it out of stock. The system identifies this and recommends similar dresses in the same size or colour based on SKU data.
An effective SKU system improves your e-commerce business’ inventory management. In addition, it also provides valuable sales insights to help you improve the shopping experience for your customers. Benefits like this contribute to increased efficiency, better decision-making, and improved profitability in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
How to create SKU numbers?
Creating an efficient SKU system is important for streamlining your inventory management, especially when working with UK fulfilment services. There are no strict rules, but here are some tried-and-tested tips to generate SKU numbers:
1. Set a Standard Naming Convention
A consistent SKU structure makes it easy to manage and interpret your inventory. Here’s how you can do it:
- Start with a prefix that identifies the product category.
- Use logical codes for attributes like size, colour, and style.
- Keep SKUs between 8-12 characters for optimal readability.
2. Ensure uniqueness of SKUs
Avoiding duplicate SKUs is crucial for accurate inventory tracking. Here are some best practices:
- Use a combination of letters and numbers to make each SKU unique.
- Avoid easily confused characters (e.g., 0 and O, 1 and I).
- Implement a system to check for duplicates when creating new SKUs.
3. Showcase similar products together
Grouping SKUs for similar products can simplify inventory management and restocking. For example, all men’s blue t-shirts could have SKUs starting with ‘MTB’, followed by size and specific style codes.
Include Essential Product Information
Incorporating relevant data in your SKUs helps with logistics and fulfilment. Consider adding:
- Dimensions or weight categories.
- Codes for special handling requirements.
- Location codes if you manage multiple warehouses.
Here’s an example of a well-structured SKU code:
MTB-L-001-F-WH1
- MTB: Men’s T-Shirt Blue
- L: Large size
- 001: Specific style number
- F: Fragile item
- WH1: Warehouse 1
By following these guidelines, you can create a robust SKU system that enhances your inventory management, improves order accuracy, and boosts your e-commerce efficiency. Green Fulfilment can help you implement and manage this system effectively, ensuring seamless integration with their fulfilment warehouse operations.
SKU Management Systems
As your e-commerce business grows, managing SKU numbers can become increasingly difficult. The right SKU management software offers robust solutions for inventory control and order fulfilment.
SKU management systems are specialised tools designed to streamline the creation, tracking, and analysis of stock keeping units. These platforms integrate with your existing inventory management processes. They give you a centralised hub for all SKU-related activities.
Key features that you need to look for in SKU management tools include:
- Automated SKU generator
- Real-time inventory tracking
- Sales data analysis
- Integration capabilities
- Barcode scanning
- Reporting tools
Automating SKU tracking and management improves accuracy by reducing human error in SKU creation and data entry. It saves time by automating repetitive tasks, freeing up staff for other activities. Enhanced visibility provides real-time insights into stock levels and product performance, which leads to better decision-making for inventory planning and purchasing.
When choosing an SKU management system, consider your business’s specific needs, budget, and growth plans. Look for solutions that offer scalability and can integrate with your existing systems. Green Fulfilment’s expertise in fulfilment services can help you select and implement a system that aligns with your business goals and integrates seamlessly with their fulfilment warehouse operations.
An effective SKU management system improves your inventory control, streamlines your operations, and ultimately contributes to increased profitability. Making use of these tools and partnering with a reliable fulfilment centre like Green Fulfilment, you can ensure that your e-commerce business stays competitive in an increasingly complex market landscape.
Keep in mind that the goal of any SKU management system is to simplify your inventory processes, so you can focus on growing your business and meeting customer needs.
How to implement SKUs in your store
Effective implementation of SKUs in your e-commerce operations can improve your business efficiency. Let’s explore some key aspects of this process:
Setting Reorder Points
Determining when to restock is important if you want to maintain optimal inventory levels. To set effective reorder points, you need to:
- Analyse historical sales data for each SKU.
- Consider lead times from suppliers.
- Factor in seasonal demand fluctuations.
For example, a popular T-shirt SKU might have a reorder point of 50 units, triggering a new order when stock drops to this level. Lots of fulfilment centre software solutions, including those used by Green Fulfilment, can automate this process. The software sets up alerts for low stock levels and generates purchase orders automatically.
Packaging and Shipping Requirements
Incorporating packaging information into your SKU system can streamline your warehouse fulfilment process. Add codes for specific packaging types (e.g., ‘BX’ for box, ‘PL’ for polybag) and include handling instructions (e.g., ‘FR’ for fragile). For instance, a SKU for a delicate vase might end with ‘BX-FR’, indicating it needs a box and careful handling.
How do you ensure proper handling?
- Train staff on SKU interpretation
- Use SKU data to guide packing decisions
- Implement quality control checks based on SKU information
Green Fulfilment’s experienced team can help you develop and implement these SKU-based packaging strategies, ensuring efficient and accurate order processing.
Real-time Inventory Monitoring
Real-time tracking is important. It prevents stockouts and ensures customer fulfilment. It also delivers accurate stock levels across all sales channels, allowing for immediate action on low-stock items. It also supports dynamic pricing based on inventory levels.
Tools and technologies for real-time inventory management include RFID systems for instant stock updates, cloud-based inventory software for multi-location tracking, and mobile apps for on-the-go inventory checks. Green Fulfilment’s advanced systems integrate seamlessly with these technologies, providing you with up-to-the-minute inventory data.
Executing these SKU-based strategies in your e-commerce operations does wonders for your inventory management. It reduces errors and enhances customer satisfaction. Whether you’re managing your own warehouse or working with fulfilment companies like Green Fulfilment, a well-implemented SKU system can be the backbone of efficient e-commerce operations. It enables you to maintain optimal stock levels, ensure proper product handling, and respond quickly to changing market demands.
What are some alternatives to SKU numbers?
SKU numbers are important for internal inventory control, but there are other ways for retail products to be identified. Let’s have a look at some substitutes and evaluate how they stack up against SKUs.
SKU vs. UPC
Universal Product Codes (UPCs) are a popular method of product identification. Although SKUs and UPCs share some similarities, and even if they’re often used together, both of these product identification methods serve different purposes.
SKUs are internal codes that specific retailers and fulfilment centres use. Typically, they consist of 8 to 12 alphanumeric characters. They are customised to fulfil certain company requirements. The colour, size, and style of a product can be identified with the use of SKUs.
UPCs are standardised 12-digit numeric codes that are used by many retailers and supply chains. They provide the name of the manufacturer and the specific item, but don’t offer detailed product characteristics. UPCs are issued by GS1 — a global organisation that manages various standards.
SKU vs. Barcode
Barcodes visually represent data. They are capable of encoding various types of information and are composed of parallel lines with varying lengths. They can house SKU information for faster data entry and scanning..
Unlike SKUs, which are created by retailers or fulfilment warehouses, barcodes for UPCs are standardised and assigned to products regardless of where they’re sold. However, many retailers generate barcodes that represent their SKUs for internal use..
SKU vs. Serial Number
Serial numbers are also product identifiers and they serve a different purpose from SKUs.
SKUs can be shared by multiple units of the same product and can be used to identify a certain product type. For instance, a specific style’s medium-sized red t-shirts would all share the same SKU.
Serial numbers are specific to each unit of a given product. Manufacturers use them to keep track of certain products for recalls, repairs, and warranty claims. They’re quite helpful for expensive goods or products that might require maintenance.
The differences between SKUs, UPCs, barcodes, and serial numbers are explained in detail below:
| Identifier | Purpose | Characteristics |
| SKU | Internal inventory management | Alphanumeric, 8-12 characters, tailored to specific business needs |
| UPC | Standardised identification across retailers and supply chains | Numeric, 12 digits, identifies manufacturer and specific item |
| Barcode | Visual representation of data (e.g., SKUs, UPCs) | Parallel lines of varying widths, can encode various types of information |
| Serial Number | Unique identification of individual product units | Numeric or alphanumeric, unique to each product unit |
FAQs on SKU Numbers
What is SKU in logistics?
SKUs are a special identification number used to identify any product or service that is available for purchase. Because it makes precise inventory tracking, effective stock management, and streamlined order fulfilment processes possible, it is important to the supply chain.
SKUs are very helpful in warehouses. They help staff find and choose items for shipping more quickly. In addition, they also support data analysis, which enables companies to monitor sales patterns and make informed decisions for restocking and product offerings
How to calculate SKU?
SKUs aren’t calculated in the conventional sense. Instead, they are developed based on specific product attributes. The process of SKU creation involves developing a standardised format with relevant details like product category, size, colour, and other distinguishing features.
Businesses should use a combination of letters and numbers, create a clear naming convention, and make sure each SKU is distinct inside their system in order to produce effective SKUs. Many companies use automated tools or inventory management software to generate SKUs, ensuring consistency and reducing the risk of human error.
How to generate SKU Numbers?
The first step in creating SKU numbers is a clear and standardised naming convention that represents your product line and business needs. Usually, this involves building a structure with details like the product category, attributes like size or colour, and a unique identifier.
After setting up your system, you can manually create SKUs for each product or utilise a SKU generator tool. (SKU generator tools are often included in inventory management software). Automating the SKU creation process ensures that every SKU is unique and follows your preset format. Consistency and clarity are keys to a successful SKU structure.
What are the 4 types of SKU?
SKUs can be categorised according to their origin and purpose, even though there aren’t any precise “types” of them.
- Manufacturer SKUs: Designed by manufacturers of products and often used across multiple retailers.
- Retailer SKUs: May be more specific and developed by individual buisnesses for internal use.
- Global Trade Item Numbers (GTINs): These are standardised numbers used in international trade.
- Custom SKUs: Tailored for a company’s unique requirements. They also usually include more thorough product details.
Each type serves different purposes in the supply chain and inventory management process.
What is the difference between SKU and item number?
An item number is typically a broader identifier created by the manufacturer, but an SKU is a retailer-specific identifier that contains detailed product attributes. SKUs are made for retailers to use internally, giving them more precise inventory and sales tracking.
On the other hand, item numbers are frequently more straightforward and used across multiple retailers. They could point to a general product, but SKUs go further into particular variations, such as colour or size. This distinction lets retailers manage their inventory more effectively while still communicating with suppliers using standardised item numbers.
Final Thoughts
SKU numbers are vital tools that refine inventory management, boost customer satisfaction, and improve your e-commerce operations. Effective inventory systems are becoming more and more crucial for corporate success as internet markets expand.
At Green Fulfilment, we understand how a well-implemented SKU system can streamline a company’s operations. SKUs are essential to the success of e-commerce because they reduce fulfilment errors and provide insightful business data. Use SKUs effectively and let your inventory management be a major asset to your business.
